To find out about the most suitable vision correction option, register for a visit, or find out other important information, leave your contacts, and we will contact you as soon as possible.
Visit to an ophthalmologist and diagnostic examinations
It all starts with a visit to an eye doctor. At the first and full eye and vision health examination, you will have:
- visual acuity test;
- refraction;
- intraocular eye pressure control;
- biomicroscopic examination of the anterior parts of the eye;
- direct ophthalmoscopy;
- indirect ophthalmoscopy;
- final diagnosis;
- therapy prescription.
After examination and test results, you may be appointed to additional tests if necessary.
CAUTION!
It should be noted that during eye examinations, pupil dilating drops are used, which can reduce visual acuity for up to 3-4 hours, so it is recommended to avoid driving during this period, as well as performing other work where clear vision is required. Vision can also be challenging when reading.
When should a child's eyes and vision be checked?
The child's visual system fully develops by the age of 7-8. Suppose a disorder prevents the information from the eye from entering the central nervous system in the brain during this period. In that case, the development of vision may be delayed or incomplete.
The earlier the disorder is detected and corrected, the greater the chances of gaining full vision.
How does the doctor examine the child's vision?
Many parents are surprised to learn that even a tiny child can have a complete vision test. An experienced ophthalmologist can also assess the visual acuity of a child who has not yet spoken by examining how the child captures the view and follows bright lights and small toys. It is essential to check each eyelet individually. For slightly older children, special puzzle-type symbols are used to assess vision. It is also necessary to check the binocular vision function, evaluate whether there is strabismus, and check the eye movements.
What questions does the doctor ask on the first visit?
The doctor needs to know if there have been any complications during pregnancy, if the births have taken place at the scheduled time, or if there have been any complications in their course. Need to know about the child's general health problems, the operations performed, and the existing allergies. It is also important to know about eye diseases in the family.
Why is it necessary to use eye drops during your visit?
One of the most critical components of the test is the use of special pupil-expanding eye drops to assess the amount of refraction or refraction of the eye by relaxing the accommodation muscle. This is necessary to accurately determine the degree of existing farsightedness, nearsightedness or astigmatism and to assess the extent to which these readings correspond to the child's age norm. The dilated pupil also makes it easier to see the eyelid's internal structures and are not harmful to the child's health.
What are the most common vision problems in children?
The most common problems that can interfere with normal vision development in children are strabismus, amblyopia or "lazy eye", and refraction problems.
Strabismus is a pathology when both eyes are directed in different directions. One eye can be directed either inwards or outwards, up or down, while the other is fixed centrally. Strabismus can be continuous or intermittent. It can interfere with the development of vision and prevent the development of spatial or depth vision. It can also be a cosmetic problem.
Amblyopia, or "lazy eye", means impaired vision in one or both eyes that cannot be corrected with glasses or lenses. It develops in infancy or early childhood - this is the most sensitive period of a child's vision development. The earlier amblyopia is detected and treated, the better the result. After 7-8 years, amblyopia can no longer be cured.
Amblyopia is caused by any cause that prevents the image from entering the retina through the eye's optical system. The most common causes of "lazy eye" are:
- peculiarities of refraction;
- strabismus;
- eye transparent environmental diseases that do not allow the image to be accurately projected on the retina.
To treat amblyopia, it is necessary not only to eliminate its cause (for example, wear glasses, surgery for strabismus or cataracts) and make the "lazy eye" work harder - watch. This is achieved by sealing the whole, better-seeing eye with a special occluder (eye patch) at a certain time of the day.
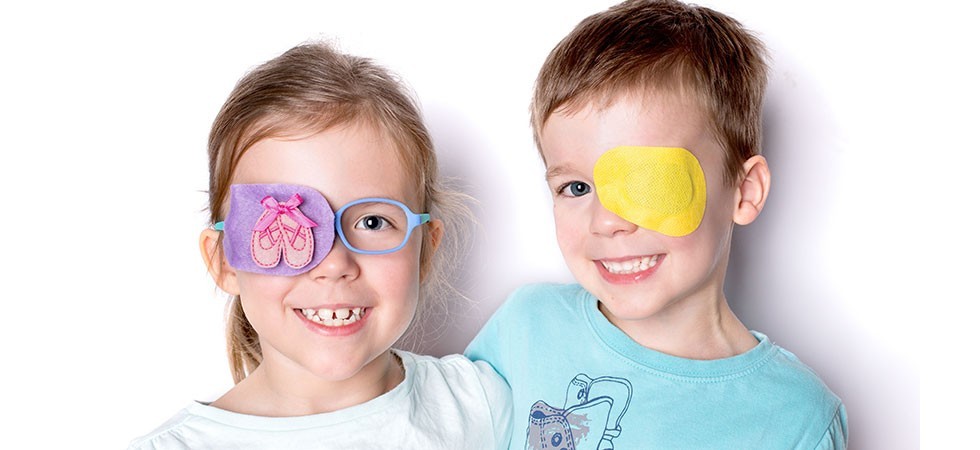

How to help a child's eyes?
Today, digital technologies have also become an integral part of children's lives, both at home and school. However, these are relatively new, and long-term effects on the child's eyesight are still being elucidated.
To reduce the impact of unwanted computer devices on the child's eyes, the frequency and duration of their use should be controlled.
The eye, like any organ, gets tired of doing one job for a long time. Many vision specialists and educators recommend a short rest for long-term work.
Very simple! Everything to remember:
20 - 20 - 20
take a 20-second break every 20 minutes, looking at 20 feet *.
* 20 feet = 6,096 meters
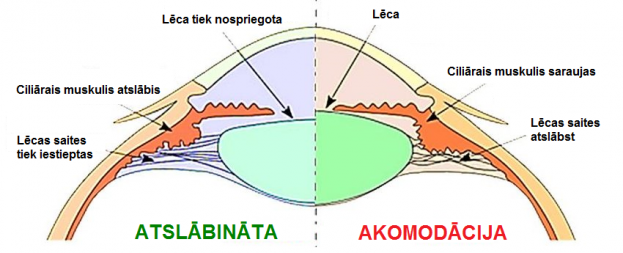
If the child is working looking nearby for a long time, the eye's ciliary muscle is employed, and spasms can sometimes develop.
Due to fatigue, the eye loses the ability to respond to changes in focal length, as a result of which the ciliary muscle is unable to relax, accommodation spasms occur.
What do you need to know about a child's vision at different ages?
The child's eye grows with the child. The eye is believed to have grown in a person between the ages of 18 and 21. To not interfere with the eyes' growth and development, it is essential to know what is important at each stage of the child's development.
Why is it important to check your eyes during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a unique period in a woman's life. A woman's body adapts to new conditions and functions differently. Eyes are no exception.

Nowadays, there are no strict rules for mandatory vision and eye examinations during pregnancy. Still, we strongly recommend that all pregnant women schedule an eye doctor visit, especially if they have vision problems such as myopia and previous eye injuries, illnesses, or eye surgery.
One of the most common reasons why the caesarean section was previously prescribed for vision problems is a retinal disease. When the baby is squeezed during childbirth, there is a lot of muscle tension, which also puts pressure on the eyes. High levels of pressure and stress on the retina can affect its condition and cause even more damage if a retinal disease has previously been diagnosed.
Therefore, regardless of whether a woman wears glasses daily or does without them, any pregnant woman should check the retina's condition before giving birth.
As the eye and vision test process does not pose any risks to the expectant mother or baby, it can be done in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Suppose the eye doctor notices changes in the retina during the visit. In that case, the pregnant woman still has enough time before giving birth to prevent them in time, and, most likely, the delivery can take place naturally.
Women who can be at high risk:
- with a high degree of myopia, characterized by various degenerative processes in the retina and vascular tract;
- pregnant women with diabetes, autoimmune diseases, high blood pressure, toxicosis.
If the ophthalmologist detects retinal damage during the visit, the patient may undergo laser photocoagulation of the retina, limiting the damage to the retinal tissue.
It is recommended that the eyes be examined after childbirth to assess whether the retina has ruptured during delivery.
IMPORTANT! Suppose there has been a change in the retina before delivery. In that case, it is recommended that you see an ophthalmologist as soon as possible after delivery to make sure that the retinal damage has not progressed and that immediate treatment is not needed.
Can vision change during pregnancy?
Due to hormonal changes, visual acuity may fluctuate slightly during pregnancy. These complaints usually resolve after childbirth.
A common problem during pregnancy is a pronounced dry eye syndrome, which can develop due to hormonal fluctuations.
The tears' composition also changes during pregnancy, so we recommend using a high-quality artificial tear solution.
Why are regular eye and vision tests important for diabetic patients?
Diabetic eye diseases are one of the most common causes of vision loss.
The development and progression of diabetic retinopathy depend on the type of diabetes mellitus and the age at which the patient develops diabetes mellitus.
Retinal diseases can develop in any patient with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, causing only minor visual disturbances at first and even blindness later on.
Regular eye doctor visits are mandatory to control the disease as much as possible and to slow it down.
Diabetic retinopathies are based on:
- changes in the small blood vessels of the retina (the lining of the eye) caused by a long-term increase in blood sugar levels;
- squamous enlargement of the small blood vessels of the retina;
- increased vascular permeability;
- the proliferation of newly formed blood vessels and scar tissue inside and outside the retina.
Such processes result in oedema of the retina, precipitates ("hard exudates"), haemorrhages, varicose veins, cotton wool foci (including oxygen starvation zones, newly formed blood vessels, extensive vitreous haemorrhages), retinal detachment.
Newly formed blood vessels increase the pressure in the eye as they grow in the fluid reflux zone.
Retinal laser coagulation is used to treat diabetic retinopathies - it eliminates retinal oedema and newly formed blood vessels and stops further deterioration of vision.