To find out about the most suitable vision correction option, register for a visit, or find out other important information, leave your contacts, and we will contact you as soon as possible.
Glaucoma treatment
Glaucoma is a progressive eye disease, causing changes in the vision's nerve, followed by alterations in the visual field. The most frequent symptom of the illness is increased pressure in the eye.
There is a constant circulation of fluid in the eye produced by a gland called the ciliary body. Therefore there is also a particular draining area to prevent the accumulation of this fluid. If any circumstances occur to block this passage, the fluid is accumulated in the eye, causing a rise of the intraocular pressure, which may damage the vision nerve.
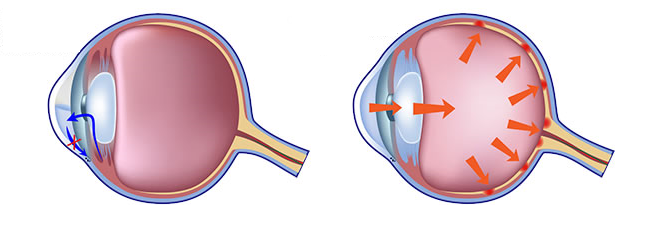
Glaucoma is one of the main causes of blindness in Latvia and around the world. But if discovered in due time, loss of vision caused by glaucoma can be almost always prevented.
Glaucoma can develop at any age, but is more common in people over 40 years of age.
How is glaucoma diagnosed?
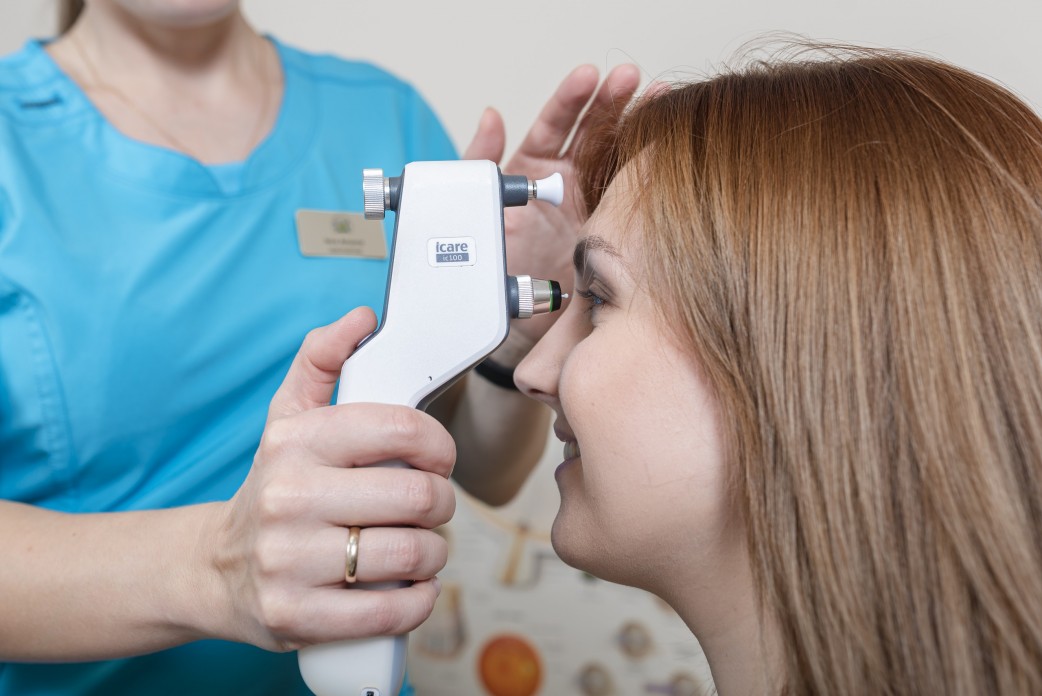
During the eye examination, the ophthalmologist measures the intraocular pressure (tonometry), examines the visual field (perimetry), measures the thickness of the cornea (pachymetry), assesses the anterior and posterior parts of the eye, including the retina and optic nerve (ophthalmoscopy), and performs other necessary examinations.
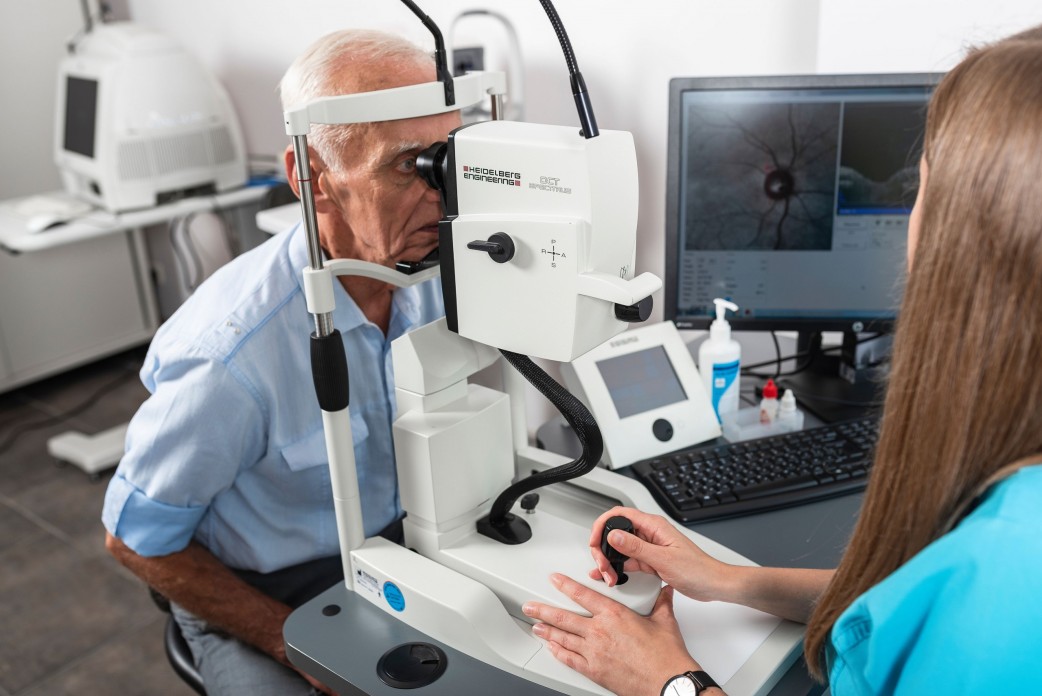
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is one of the most effective screening methods for early glaucoma diagnosis today.
It should be noted that there are also cases when the intraocular pressure is higher than normal, but there are no other symptoms of glaucoma. There are patients in whom high intraocular pressure does not cause vision loss.
Finally, after evaluating the tests' results and the patient's health, the ophthalmologist decides whether the patient needs immediate treatment or whether the patient should be registered due to suspected glaucoma.
What are the possible glaucoma treatments?
Unfortunately, the damage caused by glaucoma is irreversible, but it is possible to successfully stop the further progression of retinal and optic nerve damage, thus preserving vision.
Glaucoma can be controlled with either medication, laser or surgery.
For the treatment and follow-up of glaucoma, topical or topical drugs of the first choice are usually prescribed - eye drops, which should be used two to four times a day.
IMPORTANT! For successful results, the patient should use eye drops regularly and continuously. If necessary, eye drops are also combined with oral medications.
Surgical treatment of glaucoma is performed using laser therapy or surgery, in both cases using local anaesthesia.
Laser therapy is usually used when treatment with medication fails. The most commonly used methods for treating glaucoma are selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) and laser peripheral iridotomy (LI).
- Selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) is a fast, simple, and gentle, non-invasive laser therapy method that uses short, low-energy laser pulses to the eye. Selective laser trabeculoplasty effectively improves the intraocular fluid drainage channel's functionality and reduces intraocular pressure compared to drug treatment. This method can be safely used as an alternative to first-line medications.
- Laser peripheral iridotomy (LI) is used less frequently. It is suitable for a relatively small group of patients diagnosed with narrow-angle glaucoma or an acute glaucoma attack when the patient suffers from nausea, vomiting, and headaches and requires urgent intraocular pressure reduction.
If laser therapy has not proved effective - the patient's field of vision decreases and the eye pressure cannot be controlled - the last step in the surgical treatment is trabeculectomy.
This method provides the most significant reduction in intraocular pressure and is usually chosen for patients with moderate to severe glaucoma. Trabeculectomy is performed by creating a special filtration pad in the eye, which improves fluid drainage. This pad is usually not visible because it is hidden under the upper eyelid.
As an alternative to classical trabeculectomy, minimally invasive glaucoma surgery is now available, using various implants. One of them is, for example, a unique hydrophilic tube - XEN implant - which creates a return path for the eye fluid, thus reducing the pressure.
The type of surgery that will be performed on a patient is determined by the doctor depending on the patient's diagnosis and the disease stage.
The choice is made by considering several factors, such as whether the patient's intraocular pressure is compensated or whether the thickness of the optic nerve fibres and field of view are not reduced. Parts of the eye are also biomicroscopically evaluated, and visual acuity is checked. Of course, it is also necessary to take into account the patient's age, equality in the process of treatment, previous treatment to find out whether there have been previous eye injuries, any other eye and systemic comorbidities. Possible complications are also predicted.
IMPORTANT! The patient should bear in mind that patients with any glaucoma require periodic eye examinations, as sometimes glaucoma progresses or improves without the patient's knowledge. However, by carefully monitoring the changes in glaucoma development, timely action is possible in case of changes.
Remember - this is your vision, and you have to take care of it!
Therefore, if you have reached or exceeded the age of 40, you should see an eye doctor at least once a year.
Preventative ophthalmologist visits will help you avoid the critical consequences resulting from such a severe undetected condition as glaucoma.